Patient Resources
Brain Anatomy
About the Human Brain
Anatomy & Function
The brain is arguably the most important organ in the human body. It controls and coordinates actions and reactions, allows us to think and feel, and enables us to have memories and feelings—all the things that make us human.
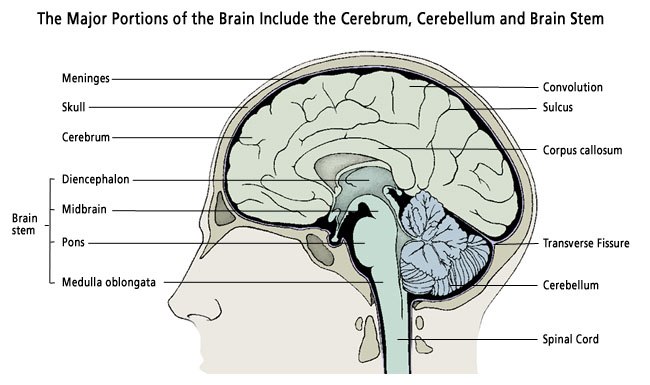
While the brain only weighs about three pounds, it is a highly complex organ made up of many parts. Years of scientific study have made it possible for scientists to identify the various areas of the brain and determine their specific functions. The following information provides a brief description of some of the major parts of the human brain.
The Cranium: Covering of the Brain
The brain is protected by a bony covering called the cranium. The cranium and the bones of the face make up the skull. Inside the cranium, the brain is surrounded by three layers of tissue called the meninges. The meninges include:
- Pia mater: The layer closest to the surface of the brain
- Arachnoid membrane: The middle layer of tissue
- Dura mater: The outer-most layer
The Cerebrum: Front Part of the Brain
The largest part of the brain, located in the front, is called the cerebrum. The cerebrum is responsible for:
- Movement
- Body temperature
- Touch
- Vision
- Hearing
- Judgment
- Reasoning
- Problem solving
- Emotions
- Learning
The cerebrum is made up of the right and left cerebral hemispheres. The hemispheres are connected at the bottom and have a deep groove running between them. In general, the right cerebral hemisphere controls the left side of the body, and the left cerebral hemisphere controls the right. The right side is involved with creativity and artistic abilities. The left side is important for logic and rational thinking.
The cerebral hemispheres are divided into lobes (broad regions of the brain). Each lobe is responsible for a variety of bodily functions. Frontal lobes are involved with personality, speech, and motor development. Temporal lobes are responsible for memory, language and speech function. Parietal lobes are involved with sensation, while the occipital lobes are the primary vision centers.
The surface of the cerebrum appears wrinkled and is made up of deep grooves (called sulci) and bumps or folds (called gyri). The outer part of the cerebrum is called gray matter and contains nerve cells. The inner part is called white matter and contains connections of nerves.
The Brainstem: Middle of the Brain
The brainstem is located in front of the cerebellum. Think of the brainstem like a computer hard-drive. It is the body’s main control panel and is responsible for conveying messages between the brain and other parts of the body. The cerebrum, the cerebellum and the spinal cord are all connected to the brainstem. The brainstem has three main parts: the midbrain, the pons and the medulla oblongata.
The brain stem controls these vital body functions:
- Breathing
- Consciousness
- Cardiac function
- Involuntary muscle movements
- Swallowing
- Eye and mouth movement
- Sensory relay (pain, heat, noise, etc.)
- Hunger
The Cerebellum: Back of the Brain
Behind the cerebrum at the back of the head lies the cerebellum. In Latin, cerebellum means “little brain,” but the cerebellum actually contains more nerve cells than both hemispheres combined. The cerebellum is primarily a movement control center, responsible for:
- Voluntary muscle movements
- Fine motor skills
- Maintaining balance, posture & equilibrium
Unlike the cerebrum, the left cerebellum controls the left side of the body, and the right cerebellum controls the right side of the body.
Other Key Parts of the Brain
Ventricular System
The brain is not a solid organ. Instead, there are fluid-filled cavities within the brain called ventricles. The ventricles provide nourishment to the brain. The ventricular system produces and processes cerebrospinal fluid, a clear, watery substance flowing around the brain to cushion and protect it.
Cranial Nerves
The brain also contains 12 pairs of cranial nerves. Each is responsible for specific body functions.
- Olfactory nerve: Sense of smell
- Optic nerve: Vision
- Oculomotor: Eye movement, eyelid opening
- Trochlear: Eye movement
- Trigeminal: Facial sensations & chewing
- Abducens: Eye movement
- Facial: Taste & facial expressions
- Vestibulocochlear: Hearing & balance
- Glossopharyngeal: Taste & swallowing
- Vagus: Swallowing & taste
- Accessory: Neck & shoulder muscles
- Hypoglossal: Tongue movement
Learn More About the Brain
To learn more about the anatomy and function of the brain, take advantage of these reputable resources:
Princeton Brain, Spine & Sports Medicine knows that many of our patients like to research their condition and treatment
and look for useful resources on the internet. However, many find this a frustrating experience.
Princeton Brain, Spine & Sports Medicine is pleased to offer you a unique health and wellness search service for internet
information that:
- Allows you to be an intelligent efficient user of the internet for health information
- Allows you to
find resources for top health and wellness sites in one place that are relevant to your
questions - Allows you to find resources in formats that you can "digest" and use to learn
What do you want to learn about?
To discuss brain disorder symptoms or schedule an appointment with a Princeton Brian & Spine neurosurgeon, call our New Jersey offices at 609.921.9001 or our Pennsylvania office at 215.741.3141. For your convenience, you can also connect with PBSSM staff online.
Request an Appointment
Submit an appointment request on our patient portal or contact our New Jersey and Pennsylvania campuses to speak with a patient advocate.